The December 18, 2024 issue of The New York Times included a large multimedia feature story by Marco Hernandez, under the headline 2024 Was the Most Intense Year for in a Decade. From the standpoint of utilizing online media for storytelling, it is impressive. Aerial views of the aftermath along a tornado’s path are vivid demonstrations of the destructive power of these storms.
A casual reader might be left with the impression that strong tornadoes in the United States are increasing, and that the increase is largely the result of industrial carbon dioxide changing our climate. There can be little doubt that was the intent of the feature. There can also be little doubt that the opposite is true.
Drawing on data from the Storm Prediction Center at NOAA, the article contains references to vast amounts of data on the number, location, strength, and cost of tornadoes in the United States. The numbers are big, and without context, potentially frightening. As of November 2024, there were 1762 tornadoes according to preliminary data, which killed at least 53 people across 17 states. They report estimated damage of $14 billion from just four outbreaks in the southeast in April and May alone. Yikes!
Here we can see that in terms of raw numbers of tornadoes, 2024 has the most since 2011:
 |
| Ref: https://www.spc.noaa.gov/wcm/#torgraph |
A Closer Look at the Data...
But what are the data really telling us? Is the high tornado count in 2024 part of a trend? Have tornado numbers been rising, falling, or hovering around a steady average? Is the tornado count number biased by increased detection using radar networks, and the armies of people with cell phones who fill my Facebook feed with storm chaser twister videos? Is the rising cost of damage caused by more storms, stronger storms, rising investment in affected areas, or building less resilient infrastructure?
The author acknowledges the effect of detection bias in the data:
“Tornado detection systems have improved, especially since the 1990s, allowing scientists to count tornadoes that might have gone undetected in previous years, said John Allen, a climate scientist focused on historic climatology and analysis of risk at Central Michigan University. That plays a role in the historical trend showing more tornadoes in recent decades.”
This is reference to the NEXRAD network that forms the backbone of our severe weather observation capability. The first installation was completed in 1992, and by 1997, all 159 stations were completed. Since then there have been upgrades giving the radars even higher resolution and more sensitivity to detect even the smallest tornadoes. In 2008 “super resolution” was added to the system. Between 2010 and 2013, dual polarization radar was deployed to better distinguish different types of reflected signals, from rain, snow, ice, hail, birds, bugs, leaves, or other lofted debris. Additional upgrades are in the works, allowing the radar to sweep different elevations and angles with ever better resolution and discrimination.
The Obligatory Implied Culprit: Climate Change
The introductory section of the article closes with:
“But 2024 could end with not only the most tornadoes in the last decade, but one of the highest counts since data collection began in 1950. Researchers suggest that the increase may be linked to climate change, although tornadoes are influenced by many factors, so different patterns cannot be attributed to a single cause.” (emphasis added)
Woven into the narrative of the story is the assumption that tornadoes are getting not only more frequent, but also more intense. Prof. Tyler Fricker of the University of Lousiana Monroe is quoted saying, “When you combine more intense tornadoes on average with more vulnerable people on average, you get these high levels of impact — casualties or property loss.”
Social Determinants of Tornado Outcomes
Importantly, Dr. Fricker also acknowledges that more and more lives and assets are in harms way, and that people in poorer areas, like rural Louisiana, have fewer resources to harden their homes and businesses against severe storms. Economic development and weather-resistant infrastructure go hand-in-hand. The same storm hitting the same population in a wealthy area will endanger fewer people who will recover quicker than a poor area which may not rebuild for years, if ever. There are many social determinants of the impact of tornadoes and other severe weather that go beyond the mere strength and number of storms. The difference between the map of where the tornadoes are, and where the tornado-related fatalities are makes this clear.
It is important to keep in mind the human impact of tornadoes. These are not just numbers. People and communities can be devastated by a tornado outbreak. But the numbers can and should help guide public policy to make sure people get the protection they need, and we are not misled by biased information. There have always been tornadoes, and there always will be. We should be prepared.
Painting with an Orange Brush
Much of the story focuses less on the number of storms and more on their location. The centerpiece of the data presented in the article is a county-by-county map of the 48 contiguous states that shows how the number of tornadoes in each county from 2002-2022 compares with 1981-2001. Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Arkansas figure prominently with disproportionate numbers of counties in shades of orange, indicating more storms. This is based on the NOAA data of every verified tornado in the United States from 1950-2023. [REF: https://www.spc.noaa.gov/wcm/data/1950-2023_all_tornadoes.csv ]
 |
| Source: Hernandez, Marco. "2024 Was the Most Intense Year for in a Decade." New York Times, December 18, 2024. |
The baseline period of 1981-2001 is a problem because we know it is affected by the improved detection of small tornadoes over that time. Even though the article acknowledges detection bias as an issue, when it comes to presenting data to the reader visually, nothing is done to correct for that bias. The vast majority of counties show an increase in the number of tornadoes from 2002-2022 relative to that artificially low baseline.
Quantifying the Bias in the Data
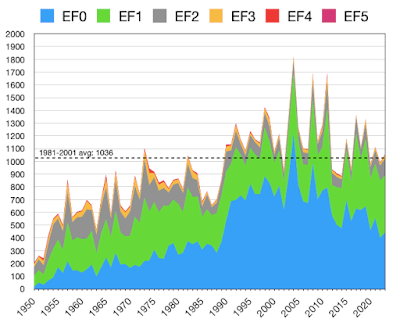
We are able to quantify the bias by looking at historical trends in the detection of tornadoes of different strengths. Like many destructive natural phenomena, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, asteroid strikes, or avalanches, tornadoes follow an approximate power-law distribution. This has been studied by Elsner et al. [Ref: J B Elsner et al 2014 Environ. Res. Lett. 9 024018 ] The power-law, also called the “1/f law”, states that the frequency of an event is inversely proportional to its power. Stated simply, a tornado that is 10 times as powerful will occur 1/10th as often. For this reason, there are roughly 2 times more EF0 than EF1 tornadoes, 3 times more EF1 than EF2, 3.5 times more EF2 than EF3, 4 times more EF3 than EF4, and 11 times more EF4 than EF5.
This chart shows the recorded tornadoes by EF category. You can see that the upward trend is driven by weaker storms. Relative to EF0-2 storms, EF3-5 are barely visible at the top margin, but they are responsible for most of the harm to life and property.
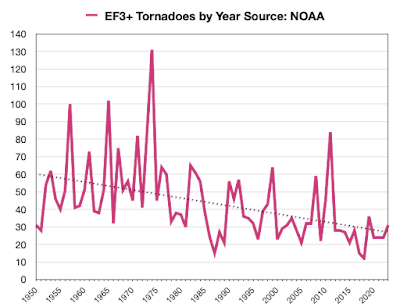
If we look at the frequency of EF3+ tornadoes as a share of the total, we immediately see the problem. It starts at around 10-15% in the 1950s, and shrinks to around 2-3% after 2000.
Unless you believe there has been a change in the power-law distribution of tornadoes causing tornadoes to trend weaker over time, you have to accept that the data for EF0-2 tornadoes is contaminated by detection bias. One way to correct for this bias is to focus on EF3 and stronger tornadoes. They are far less likely to have been missed in the 1980s, and they are responsible for the vast majority of human impact. If we focus on just the most destructive tornadoes with EF3 and above, we see the trend towards more tornadoes goes away, and actually reverses.
A Clearer Picture Emerges
When you compare the yearly rate of EF3+ tornadoes to the yearly tornado-related fatalities, it becomes clear that these are the tornadoes that are almost entirely responsible for the loss of life. Notable in the data is the tragic 2011 "super outbreak" in the vulnerable states of Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennesee which made that the worst year for tornado related fatalities in over 60 years.
Tornado track length biases the data further. Prior to the NEXRAD network, the path length of a tornado was measured largely by ground observations. With sensitive radar instruments, it is much easier to track a tornado through multiple rural counties, increasing the county count, without increasing the number of tornadoes. This is not speculation. We can see a rise in the average reported track lengths of EF3+ tornadoes in the data.
This graph requires a little explanation. The blue line is the average track length for all reported and measured tornadoes from 1950-2023. The green line is average of just the EF3+ tornadoes. Since weaker tornadoes have shorter tracks, the detection bias over time for weak tornadoes drives the average down. But looking at just the EF3+ tornadoes, the average length rises after 2000. This is due to improved tracking of stronger tornadoes as they travel and pass into the weaker phase of their life cycle.
No Increase in Tornadoes, But Is Their Location Shifting?
The NOAA data convincingly demonstrates that there is no sign of tornadoes getting stronger or more frequent, and to the extent there is a trend, it is towards fewer of the most destructive tornadoes. However, there is some reason to believe that the center of tornado activity has moved a little south and east. The table below aggregates the county data used in the orange map above into states. Then it accounts for bias by counting only EF3, 4, and 5 tornadoes. There are a few surprises. Florida, goes from a major decrease to a significant increase, while Kansas, Minnesota, Iowa, and Oklahoma go from big increases to big decreases. This reinforces the hypothesis that tornadoes are trending southeast. The unbiased accounting shows a trend towards increased strong tornadoes in places like Alabama, Mississippi, Georgia, North Carolina, and fewer in the more northwestern hotspots of Kansas, Iowa, Oklahoma, Nebraska, Minnesota, and South Dakota.
If tornadoes really are trending more to the south and east over time, due to changes in atmospheric patterns, this should have some policy implications. The infrastructure in these areas is not as hardened against severe weather than in places where severe weather has historically been more common. Also, these are some of the most economically disadvantaged regions of our country.
Building for Resilience
The first and most obvious policy conclusion is that the energy and transportation infrastructure in these areas, especially the electric grid, should not be dependent on the weather for power. To the extent that the electric grids in these areas use weather-dependent solar and wind energy, they become both unreliable and more vulnerable to storms, which can shatter solar photovoltaic panels with hail, and uproot them with strong winds. Wind turbine blades can become deadly projectiles, in addition to being destroyed. Mission critical vehicles should not be dependent on the electric grid to refuel. Building out nuclear baseload capacity and natural gas power supply for peak demand will go a long way towards making energy reliable and affordable in all weather. Even 100% reliable and dispatchable power generation can not reach the people who need it if the transmission lines are down. But a downed transmission line can be repaired much more quickly and cheaply than a wrecked wind farm or solar array.
Source: @LiveStormsMedia
The good news is that there is no reason to believe that tornadoes in the United States are getting more frequent or stronger. The bad news is that regions of the country that should be making their infrastructure more resilient to the kinds of weather that will always come around eventually are instead making their energy infrastructure, and people, more vulnerable. This is the story that The New York Times could have told their readers. Instead, they left their readers with the impression that tornadoes are getting worse, and that solar panels and wind turbines could make them safer, when the exact opposite is true.
***